
The advantages and disadvantages of Blockchains must be kept in mind while making a decision to shift to blockchain-based applications. Blockchain has taken the world by storm. All major industries and organizations are striving to adapt to blockchain technology.
Blockchains are the backbone of crypto and web 3.0. There are some inherent issues with web 3.0 applications however, most of them are related to blockchains problems. We are going to discuss the advantages that blockchains provide and then discuss some problems of blockchains.
Table of Contents
Advantages and Disadvantage of Blockchains Explained
Aim of the Blockchains
The main Aim of the Blockchains is the “exchange of electronic cash between peers without relying on any trusted third party and prevent double-spending or reversible transactions”. (NAKAMOTO 2008)
The blockchains have evolved a lot from providing decentralized currency to now controlling supply chains, providing security to IoTs and smart cities.
Now let us see the major Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain.
Advantages of Blockchain | Blockchain benefits
Blockchain provided a new dimension to solve our daily problems. The main advantages that blockchain provides include the following:-
- Decentralization
- Avoids single point of failure
- Unforgeable
- Trustless operation
- Cryptographic security
- Low Transaction cost
- Transparency
- Immutability
- Free from censorship
- Verifiable
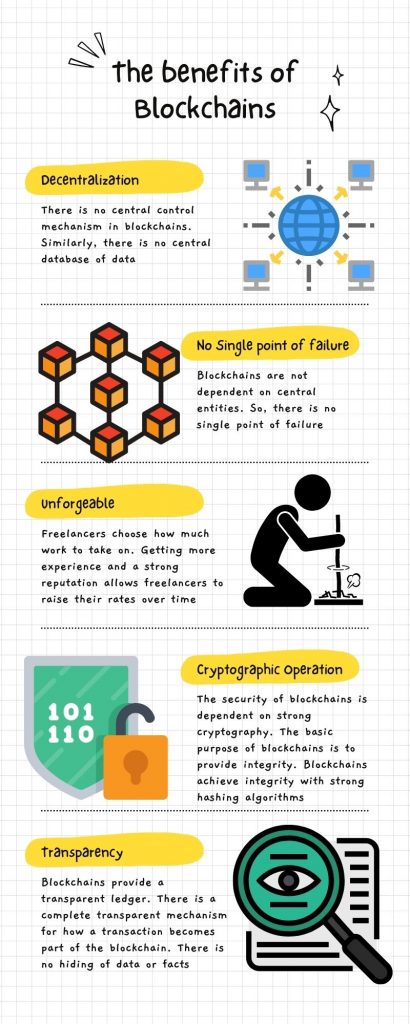
1. Decentralization
The biggest advantage of blockchains is decentralization. There is no central entity in blockchain to control your data. Blockchain provides two prone decentralization:-
- Decentralization of control
- Decentralization of Data
There is no central control mechanism in blockchains. Similarly, there is no central database of data. In today’s world, most of the data is being controlled by major entities like Google, Facebook (now Meta), or other social media sites. They control the data and can do whatever they want with the data. They have control.
In blockchains, there is no central control with the governments or companies, and no one can control or censor your data. Similarly, they don’t own your data. Most of the advantages of blockchains stem from decentralization. Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) are becoming popular to avoid centralized control.
2. No Single point of failure
Blockchains are not dependent on central entities. So, there is no single point of failure. In Web 2.0, we are mostly reliant on central databases and servers which are prone to failure due to some natural calamity or malicious attacks. In blockchains, the copies of the blockchain are stored at nodes, so, there is no single point of failure.
3. Unforgeable
The record on blockchains is unforgeable. Once a transaction becomes part of the blockchain, anyone can verify it. No one can forge a record or amend the record.
4. Trustless operation
In today’s world, we are dependent on tech joints for our data. In blockchains mode of operation, there is no central trusted party. We are controlling our own data. No single entity controls the blockchain operation so they operate in a trustless environment.
5. Cryptographic Operation
The security of blockchains is dependent on strong cryptography. The basic purpose of blockchains is to provide integrity. Blockchains achieve integrity with strong hashing algorithms. Some blockchains also provide confidentiality and privacy of data.
6. Low Transaction cost
The banking transactions cost too much money and taxes. Crypto transactions are fast and they cost very little as compared to banking transactions.
7. Transparency
Blockchains provide a transparent ledger. There is a complete transparent mechanism for how a transaction becomes part of the blockchain. There is no hiding of data or facts. Similarly, the code of the smart contract that deploys on blockchains is visible for everyone and no hidden code can run on blockchains.
8. Immutability
Transactions, once recorded on the blockchain, can’t be changed or deleted. All transactions on blockchain have an embedded timestamp which is a permanent record. There is no amendment of record once it becomes part of the blockchain.
9. Free from censorship
Blockchains are not controlled by any organization or government. There is no censorship. No one can control or block blockchains. So, no one controls the blockchain.
10. Verifiable
Blockchain stores data in a decentralized manner. Everyone can verify the correctness of the information being presented by any party.
Disadvantages of Blockchain
Blockchain is not without its flaws. We are already seeing issues with web3 technologies like the DAOs. The main disadvantages of Blockchain include the following:-
- Scalability
- Latency
- High Energy and communication costs
- Lack of consensus finality
- Forming of forks
- Storage
- Private keys management
- Privacy of data
- Immaturity
- Lack of Laws and Regulations
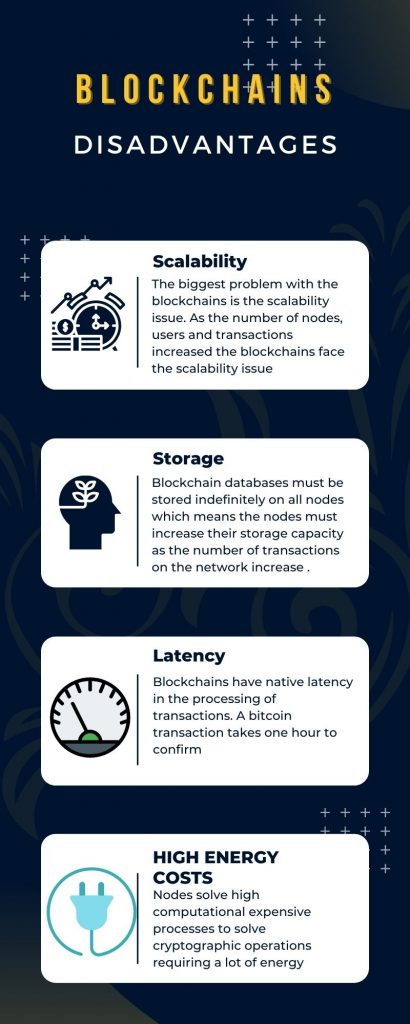
1. Scalability
The biggest problem with the blockchains is the scalability issue. As the number of nodes, users and transactions increased the blockchains face the scalability issue. Every node needs to store the complete copy of blockchains and as the users increase, blockchains face scalability issues in terms of performance.
2. Latency
Blockchains have native latency in the processing of transactions. For example in bitcoin, every transaction is confirmed after 6 blocks become part of the blockchain. One Block approximately takes 10 minutes to be added to be confirmed to blockchain. So, it needs 60 minutes to properly confirm a transaction. Now suppose you want to make a payment for a pizza, we can not wait for 60 minutes. Different blockchains have resorted to different mechanisms to confirm the issue.
3. High Energy and communication costs
Most of the blockchains employ proof of work consensus algorithm. This requires every miner node on the blockchain to solve a cryptographic puzzle to make block part of a blockchain. This is a computationally expensive process and consumes a lot of energy and power. This is the biggest reason the environmentalists are against bitcoin. Secondly, as nodes develop a consensus among each other, they must communicate with each other very frequently which consumes network bandwidth.
4. Lack of Consensus Finality
The problem is induced in the blockchains by design. To publish a new block, miner nodes present their proof of work to other nodes. Now, vetting of the work, requires some time, For example in the bitcoin blockchain, 15 minutes may be spent for the propagation of new blocks which leads to delay in consensus finality inducing delays.
5. Forming of Forks
Due to lack of consensus finality, another problem arises that is the forming of forks.
Blockchain forks are an chains that develop in different directions due to a lack of immediate consensus formality. Different miners may extend the blockchain in different directions. However, over the period of time, the forks are resolved and the longest chain is followed. The forks may also form due to an update in the protocol and some nodes may be running old version of the protocol software.
6. Storage
Blockchain databases must be stored indefinitely on all nodes which means the nodes must increase their storage capacity as the number of transactions on the network increase and the size of blockchains becomes larger and larger. The size of the database will only expand. For example, the size of the Ethereum blockchain is increasing at the speed of 55 GB/year.
7. Private Keys Management
The blockchains store only the public addresses of the crypto wallets. The private keys of the wallet are the responsibility of the user. The private keys are stored with the wallet. If a user looses the private key of the wallet, then cryptocurrency can not be extracted. It is estimated that approximately 3-5 million bitcoins have been lost to key management.
8. Privacy of Data
Everything on the blockchains in open and transparent. There is no privacy of data. Even though user identities are not part of blockchain but the public addresses of wallets are always visible and everyone knows when a large sum is moved from a wallet.
9. Immaturity
Blockchain, technology is still maturing. The work on the blockchains is still in the developing phase. People have developed different blockchains to solve different issues. Web3 products are emerging in the market but still, there are a lot of issues and scams associated with the technology. Eg:- The DAO attack in 2016 resulted in major chunk of Ethereum in hackers’ pockets.
10. Lack of Laws and Regulations
There are still many countries where there are no laws to regulate crypto and web3 products. DAOs based on blockchains have started being recognized by some states but still many countries feel inclined to block the crypto trading altogether. The recent Russia Ukraine war has given new rise to crypto popularity where Ukraine resorted to crypto for donations and Russia looking to utilize crypto to avoid financial sanctions. Still, there are many blockchain-based Ponzi schemes that must be avoided.
FAQ
What are the major advantages of blockchains?
The major advantages that blockchains provide include decentralized, transparency, lack of censorship, immutability, and trustless operation. There is no central entity controlling blockchains.
How to solve the scalability problem of blockchains?
Many new blockchains are being developed to solve the scalability problem of blockchains. People are also working on new layer 2 protocols for bitcoin to solve the scalability problem.
What is the size of the Bitcoin blockchain?
The size of the Bitcoin blockchain is approximately 350 GB. The size of the Bitcoin blockchain is increasing at the rate of 1MB per 10 minutes.
What are the major disadvantages of Blockchain?
The Major disadvantages of blockchain include scalability, latency, forming of forks, lack of consensus formality, high computation costs and privacy issues.